Home » Spreading Awareness, Fighting Against Oral Cancer
Oral cancer poses a significant health challenge in India, ranking among the top three types of cancer in the country. With age-adjusted rates at 20 per 100,000 population, contributing to more than 30% of all cancers in the country.
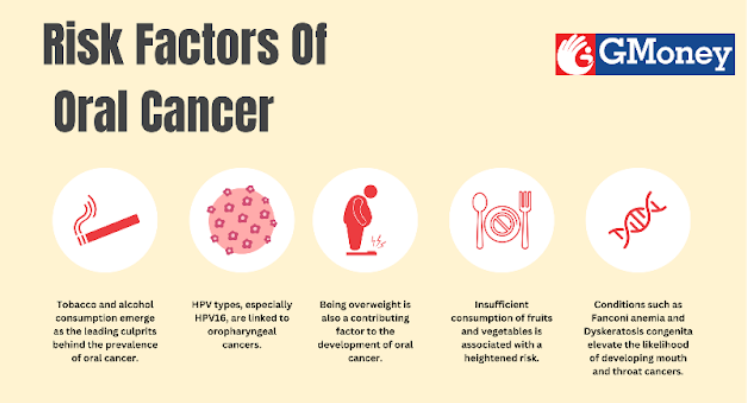
Various factors contribute to the prevalence of oral cancer in India, including the ageing population and regional variations in disease-specific risk factors.
Tobacco and Alcohol Use:
Strong risk factors for head and neck cancers, including oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancer.
Smoking and other tobacco exposure significantly increase the risk, especially with prolonged use.
Oral tobacco products Also lead to high risks, affecting the cheek, gums, and inner lips.
HPV Infection:
Certain HPV types, especially HPV16, are linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
HPV-related cancers are more common in younger individuals with multiple sex partners.
Excess Body Weight: Being overweight increases the risk of oropharyngeal and laryngeal cancers.
UV Light Exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight, a source of UV light, increases the risk of lip cancers.
Poor Nutrition: Low intake of fruits and vegetables is also linked to an increased risk.
Genetic Syndromes: Syndromes like Fanconi anemia and Dyskeratosis congenita increase the risk of mouth and throat cancers.
Betel Quid and Gutka: Chewing betel quid and gutka increases the risk of mouth cancer.
Tobacco And Alcohol Limitation
Using tobacco and alcohol significantly increases the risk of oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers. Quitting tobacco and moderating alcohol consumption are essential preventive measures.
HPV Vaccination:
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, linked to these cancers, can be reduced through vaccination. Early vaccination, ideally before sexual activity begins, helps lower the risk.
UV Light Protection:
Limiting exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, a risk factor for lip and skin cancer, is crucial. Wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can help minimize this risk.
Maintain Healthy Weight and Eating Pattern:
Adopting a healthy eating pattern with a focus on plant-based foods and maintaining a healthy weight lowers the risk of oral cancers. Following dietary guidelines contributes to overall cancer prevention.
Regular Dental Checkups:
Regular dental checkups are vital for detecting and monitoring precancerous growths like leukoplakia or erythroplakia. Early intervention and continued monitoring are essential for preventing cancer development.
Proper Denture Fit:
Ensuring dentures fit properly is crucial in preventing oral irritation and reducing the risk of oral cancer. Regular checkups and adjustments by a dentist are recommended for denture wearers.

Stage 0 (Carcinoma In Situ) Oral Cavity Cancer:
Treatment Approach: Surgery (Mohs surgery, surgical stripping, or thin resection) is the standard to remove surface-layer cancer. Regular follow-up is essential, with radiation therapy considered if carcinoma in situ recurs post-surgery.
Stages I and II Oral Cavity Cancer:
Preferred Treatments: Surgery and/or radiation therapy are effective for small cancers. Lip cancers may involve surgery or radiation alone. Surgical options include lymph node dissection if needed, and reconstructive surgery for large or deep cancers.
Stages III and IVA Oral Cavity Cancer:
Comprehensive Treatment: Surgery, including lymph node dissection, is typically the first step for larger cancers. Follow-up with radiation alone or chemoradiation is common to address residual or potentially recurring cancer.
Stages IVB and IVC Oral Cavity Cancer:
Advanced Stages: Surgery may not be viable for IVB; radiation, chemoradiation, or chemotherapy is considered. Stage IVC involves treatments like chemo, cetuximab, or immunotherapy, with a focus on symptom relief and preventing complications.
Recurrent Oral Cavity Cancer:
Addressing Recurrence: Treatment options vary based on the cancer’s location, prior treatments, and overall health. Surgery is often considered if radiation was the initial treatment. Lymph node dissection, radiation, chemoradiation, and systemic therapies like chemo or immunotherapy are tailored to the individual’s situation.
Tata Memorial Hospital
https://tmc.gov.in/index.php/en/contact-us-3
Helpline Number : – +91-22- 24177000, 24177300, 24161413
GMoney is in support with the hospitals and staff who are providing care and treatments for all the affected with lung cancer and giving them new life
At Gmoney we work with hospitals to provide Advance Against Mediclaim, No Cost EMI services For Needful Patients
For More Information Contact : https://www.gmoney.in/
Follow us
Reach us
Mumbai HO
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
315, 215 Atrium,
Next to Courtyard by Marriott,,
A.K. Road, Andheri East,
Mumbai - 400093
Ph : +91 86570 00105, +91 72089 60444
Quick Links
Bengaluru
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Oyo Work Spaces, Umiya Emporium,
Opposite Forum Mall, Hosur Rd,
Koramangala, Bengaluru,
Karnataka 560029
Ph : +91 89717 34815
Delhi
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Berry Co Works, 1E/3,
Jhandewalan extension,
Next to jhandewalan metro station
gate no. 2 Barakhambha Road,
New Delhi, Delhi 110001
Ph : +91 97116 26832
Pune
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
91 Spring Board, Sky Loft,
Creaticity Mall, Off, Airport Rd,
opposite Golf Course, Shastrinagar,
Yerawada, Pune,
Maharashtra 411006
Ph : +91 84250 28758
Chandigarh
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
SCO no. 292,
First Floor, Sector 35D,
Chandigarh
Ph : +91 84279 82012
Jaipur
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
CODESKK Civil Tower,121 122,
Pandit TN Mishra Marg,
Santhosh Nagar, Nirman Nagar,
Jaipur – 302019
Ahmedabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
22nd Floor, B Block,
Westgate By True Value,
Nr. YMCA Club, SG Highway,
Ahmedabad – 380051
Hyderabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Dwaraka Pride,
Plot no. 4/1, Survey No. 64,
Huda Techno Enclave, Madhapur,
Hyderabad (Telangana) – 500081
Chennai
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
DBS Business Center, 31A,
Cathedral Garden Rd, Badrikari, Tirumurthy Nagar, Nungambakkam, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu – 600 034
Mumbai HO
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
315, 215 Atrium,
Next to Courtyard by Marriott,,
A.K. Road, Andheri East,
Mumbai - 400093
Ph : +91 86570 00105, +91 72089 60444
Bengaluru
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
3rd floor, Ranka Junction,
AH45, Krishna Reddy Industrial Estate,
Dooravani Nagar,
Bengaluru Karnataka - 560016
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Pune
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
91 Spring Board, Sky Loft,
Creaticity Mall, Airport Rd,
Opp. Golf Course, Shastrinagar,
Yerawada, Pune,
Maharashtra - 411006
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Delhi
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Berry Co Works, 1E/3,
Jhandewalan extension,
Gate no. 2 Barakhambha Road,
New Delhi, Delhi - 110001
Ph :
+91 72089 60444
Chandigarh
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
SCO No. 292,
First Floor, Sector 35D,
Chandigarh - 160022
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Hyderabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Dwaraka Pride,
Plot no. 4/1, Survey No. 64,
Huda Techno Enclave, Madhapur,
Hyderabad (Telangana) - 500081
Jaipur
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
CODESKK Civil Tower,121 122,
Pandit TN Mishra Marg,
Santhosh Nagar, Nirman Nagar,
Jaipur - 302019
Chennai
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
DBS Business Center, 31A,
Cathedral Garden Rd, Badrikari,
Tirumurthy Nagar,Nungambakkam, Chennai,
Tamil
Nadu - 600 034
Pune | Mumbai | New Delhi | Kolkata | Chennai | Navi Mumbai| Bengaluru | Ahmedabad | Nagpur | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Bhopal | Bhubaneswar | Nashik | Indore | Ghaziabad | Kanpur | Amritsar | Vasai | Noida | Gurugram | Chandigarh | Ranchi | Cuttack | Thane | Kalyan | Jalandhar | Kolhapur | Visakhapatnam | Chakan| Greater Noida | Wagholi | Raipur | Panvel | Belgaum | Mohali | Bhiwandi | Talegaon | Coimbatore | Palghar | Mumbra | Sangli | Surat | Durgapur | Ludhiana | Kochi | Agra | Ahmednagar | Ajmer | Akola | Aurangabad | Baroda | Beed | Rewari | Patiala | Vellore | Ranjangaon | Nanded | Nellore | Panipat | Panjim | Madurai | Mysore | Mangalore | Korba | Mathura | Kalaburagi | Jalgaon | Kharar | Guwahati | Kollam | Jamshedpur | Gwalior | Saswad | Solapur | Varanasi | Salem | Sambalpur | Jodhpur | Hubli | Panchkula | Faridabad | Amravati | Ayodhya | Badlapur | Dehradun | Parbhani | Ujjain | Udaipur | Tiruchirappalli | Srinagar | Shimla | Secunderabad | Ratnagiri | Pandharpur | Ananthapuram | Buldhana | Hadapsar | Baramati | Chittoor | Darjeeling | Dhule | Fatehpur | Gandhinagar | Haridwar | Gorakhpur | Jhansi | Kanchipuram | Kartarpur | Kurukshetra | Pondicherry | Prayagraj | Bharuch | Bhusawal | Bathinda | Pathankot | Nandurbar | Niphad | Kolar | Ambala | Kota | Pendurthi | Jabalpur | Palwal | Bhilai | Bhiwani | Bilaspur | Patna | Rohtak | Phagwara | Malegaon | Vijayawada | Bikaner | Chiplun | Darbhanga | Roorkee | Bhor | Rajahmundry | Margao | Alwar | Dhanbad | Bulandshahr | Aluva | Mulshi | Davanagere | Kapurthala | Anantapur | Loni | Latur | Gondia | Chhindwara | Chandrapur | Dharmapuri-TN | Faridkot | Dharwad | Daund | Chaksu | Bareilly | Kakinada | Haldwani | Doddaballapur | Dindori-MH | Bagru | Kudus | Kozhikode | Gurdaspur | Bokaro | Berhampur | Batala | Barrackpore | Ramgarh | Meerut | Bassi | Dera Bassi | Howrah | Karjat Raigarh | Thiruvananthapuram | Bheemunipatnam | Ambegoan | Allahabad | Aligarh | Alappuzha | Tirupathi | Thoppumpady | Srikakulam | Siliguri | Rourkela | Mirzapur | Gadag | Bellary | Tumkur | Sonipat | Hoshangabad | Junnar | Jalna | Hisar | Karnal | Kottayam | Muzzafarnagar | Ramnagara | Thrissur | Bahadurgarh | Balasore | Baraut | Dhar | Ernakulam | Gadhinglaj | Chikodi | Vaniyambadi | Kamothe |