Home » Spreading Awareness, Fighting Against Cervical Cancer
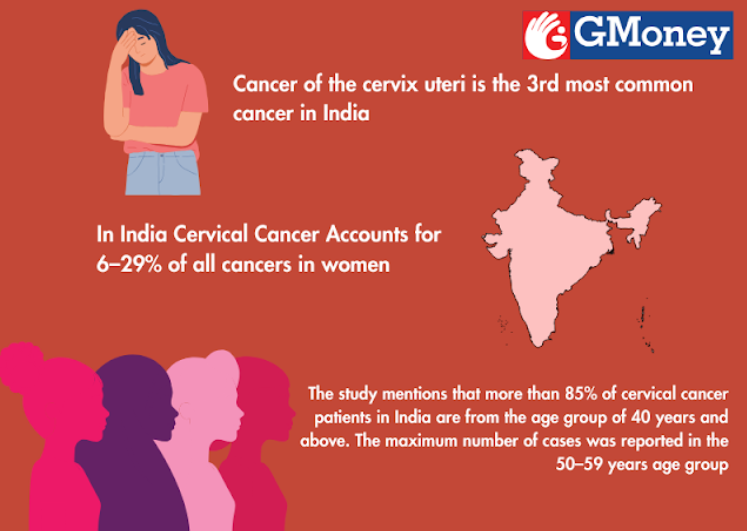
Prevalence and Scope: Cervical cancer poses a substantial burden in India, contributing to approximately 6–29% of all cancers in women. Alarmingly, India alone accounts for one-quarter of the worldwide burden of cervical cancers. It stands as a leading cause of cancer mortality, representing 17% of all cancer deaths among women aged between 30 and 69 years.
The distribution of cervical cancer incidence in India exhibits regional variations. The age-adjusted incidence rate varies widely among different regions.
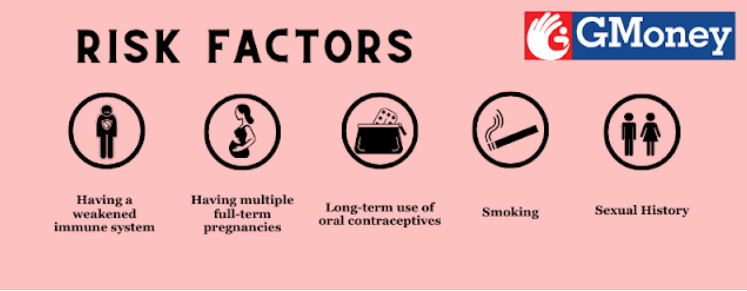
Having a weakened immune system
The immune system is important in destroying cancer cells and slowing their growth and spread. In women with HIV, a cervical pre-cancer might develop into an invasive cancer faster than it normally would.
Having multiple full-term pregnancies
Women who have had 3 or more full-term pregnancies have an increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
Long-term use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills)
There is evidence that taking oral contraceptives (OCs) for a long time increases the risk of cancer of the cervix.
Smoking
Women who smoke are about twice as likely as those who don’t smoke to get cervical cancer. Tobacco by-products have been found in the cervical mucus of women who smoke.
Sexual history
Several factors related to your sexual history can increase the risk of cervical cancer. The risk is most likely affected by increasing the chances of exposure to HPV.
Chlamydia infection
Chlamydia is a relatively common kind of bacteria that can infect the reproductive system. It is spread by sexual contact.
Young age at first full-term pregnancy
Women who were younger than 20 years when they had their first full-term pregnancy are more likely to get cervical cancer later in life than women who waited to get pregnant until they were 25 years or older.
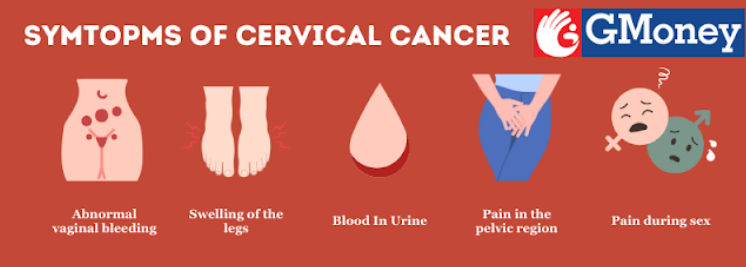
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: Irregular or unexpected bleeding outside the normal menstrual cycle.
Unusual Vaginal Discharge: Abnormal secretion from the vagina that may vary in color, consistency, or smell.
Pain During Sex: Discomfort or pain experienced during sexual intercourse.
Pelvic Pain: Aching or discomfort in the pelvic region, often persistent.
Swelling of the Legs: Abnormal enlargement of the legs, which may indicate underlying issues.
Urination or Bowel Issues: Difficulty or pain during urination or bowel movements.
Blood in the Urine: Presence of blood when urinating, potentially indicative of various health concerns.
Vaccination against HPV :- Vaccination against HPV is highly effective, with priority given to girls aged 9–14. Condom use, quitting smoking, and voluntary male circumcision also reduce HPV infection risk.
Regular Screenings :- Regular screening starting at age 30, or age 25 for women with HIV, helps detect cervical disease early.
Taking HPV Test: – Global recommendations include at least two HPV tests by age 35 and 45. Self-collection for HPV testing is a reliable option. After a positive result, treatments like thermal ablation or cryotherapy can prevent cervical cancer.
Other Preventive Measures :- Early detection and treatment of symptoms, such as unusual bleeding or pain, are crucial. Quality care involves a multidisciplinary team, adherence to guidelines, and holistic support for patients. As low- and middle-income countries expand screening, comprehensive cancer management strategies must be in place alongside prevention efforts.
Surgery:
Radiation Therapy:
Chemotherapy:
Targeted Therapy:
Immunotherapy:
GMoney extends support to hospitals and healthcare professionals dedicated to Cervical cancer care. Let’s raise awareness, advocate for screenings, and stand united with those on their journey to recovery. 💛🍽️ #CervicalCancerAwareness #EarlyDetectionSavesLives
P.D. Hinduja National Hospital and Medical Research Centre:
Helpline Number: 022 24452575 / 09820885000
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital
Visit Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital
Helpline Number: 1800 3000 3333
Tata Memorial Hospital
Helpline Number: +91-22- 24177000, 24177300, 24161413
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8819855/#:~:text=Jammu
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/cervical-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/cervical-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-symptoms.html
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer
Follow us
Reach us
Mumbai HO
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
315, 215 Atrium,
Next to Courtyard by Marriott,,
A.K. Road, Andheri East,
Mumbai - 400093
Ph : +91 86570 00105, +91 72089 60444
Quick Links
Bengaluru
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Oyo Work Spaces, Umiya Emporium,
Opposite Forum Mall, Hosur Rd,
Koramangala, Bengaluru,
Karnataka 560029
Ph : +91 89717 34815
Delhi
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Berry Co Works, 1E/3,
Jhandewalan extension,
Next to jhandewalan metro station
gate no. 2 Barakhambha Road,
New Delhi, Delhi 110001
Ph : +91 97116 26832
Pune
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
91 Spring Board, Sky Loft,
Creaticity Mall, Off, Airport Rd,
opposite Golf Course, Shastrinagar,
Yerawada, Pune,
Maharashtra 411006
Ph : +91 84250 28758
Chandigarh
GMoney Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
SCO no. 292,
First Floor, Sector 35D,
Chandigarh
Ph : +91 84279 82012
Jaipur
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
CODESKK Civil Tower,121 122,
Pandit TN Mishra Marg,
Santhosh Nagar, Nirman Nagar,
Jaipur – 302019
Ahmedabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
22nd Floor, B Block,
Westgate By True Value,
Nr. YMCA Club, SG Highway,
Ahmedabad – 380051
Hyderabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Dwaraka Pride,
Plot no. 4/1, Survey No. 64,
Huda Techno Enclave, Madhapur,
Hyderabad (Telangana) – 500081
Chennai
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
DBS Business Center, 31A,
Cathedral Garden Rd, Badrikari, Tirumurthy Nagar, Nungambakkam, Chennai, Tamil
Nadu – 600 034
Mumbai HO
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
315, 215 Atrium,
Next to Courtyard by Marriott,,
A.K. Road, Andheri East,
Mumbai - 400093
Ph : +91 86570 00105, +91 72089 60444
Bengaluru
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
3rd floor, Ranka Junction,
AH45, Krishna Reddy Industrial Estate,
Dooravani Nagar,
Bengaluru Karnataka - 560016
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Pune
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
91 Spring Board, Sky Loft,
Creaticity Mall, Airport Rd,
Opp. Golf Course, Shastrinagar,
Yerawada, Pune,
Maharashtra - 411006
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Delhi
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Berry Co Works, 1E/3,
Jhandewalan extension,
Gate no. 2 Barakhambha Road,
New Delhi, Delhi - 110001
Ph :
+91 72089 60444
Chandigarh
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
SCO No. 292,
First Floor, Sector 35D,
Chandigarh - 160022
Ph : +91 72089 60444
Hyderabad
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
Dwaraka Pride,
Plot no. 4/1, Survey No. 64,
Huda Techno Enclave, Madhapur,
Hyderabad (Telangana) - 500081
Jaipur
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
CODESKK Civil Tower,121 122,
Pandit TN Mishra Marg,
Santhosh Nagar, Nirman Nagar,
Jaipur - 302019
Chennai
GMoney Pvt. Ltd.
DBS Business Center, 31A,
Cathedral Garden Rd, Badrikari,
Tirumurthy Nagar,Nungambakkam, Chennai,
Tamil
Nadu - 600 034
Pune | Mumbai | New Delhi | Kolkata | Chennai | Navi Mumbai| Bengaluru | Ahmedabad | Nagpur | Hyderabad | Jaipur | Lucknow | Bhopal | Bhubaneswar | Nashik | Indore | Ghaziabad | Kanpur | Amritsar | Vasai | Noida | Gurugram | Chandigarh | Ranchi | Cuttack | Thane | Kalyan | Jalandhar | Kolhapur | Visakhapatnam | Chakan| Greater Noida | Wagholi | Raipur | Panvel | Belgaum | Mohali | Bhiwandi | Talegaon | Coimbatore | Palghar | Mumbra | Sangli | Surat | Durgapur | Ludhiana | Kochi | Agra | Ahmednagar | Ajmer | Akola | Aurangabad | Baroda | Beed | Rewari | Patiala | Vellore | Ranjangaon | Nanded | Nellore | Panipat | Panjim | Madurai | Mysore | Mangalore | Korba | Mathura | Kalaburagi | Jalgaon | Kharar | Guwahati | Kollam | Jamshedpur | Gwalior | Saswad | Solapur | Varanasi | Salem | Sambalpur | Jodhpur | Hubli | Panchkula | Faridabad | Amravati | Ayodhya | Badlapur | Dehradun | Parbhani | Ujjain | Udaipur | Tiruchirappalli | Srinagar | Shimla | Secunderabad | Ratnagiri | Pandharpur | Ananthapuram | Buldhana | Hadapsar | Baramati | Chittoor | Darjeeling | Dhule | Fatehpur | Gandhinagar | Haridwar | Gorakhpur | Jhansi | Kanchipuram | Kartarpur | Kurukshetra | Pondicherry | Prayagraj | Bharuch | Bhusawal | Bathinda | Pathankot | Nandurbar | Niphad | Kolar | Ambala | Kota | Pendurthi | Jabalpur | Palwal | Bhilai | Bhiwani | Bilaspur | Patna | Rohtak | Phagwara | Malegaon | Vijayawada | Bikaner | Chiplun | Darbhanga | Roorkee | Bhor | Rajahmundry | Margao | Alwar | Dhanbad | Bulandshahr | Aluva | Mulshi | Davanagere | Kapurthala | Anantapur | Loni | Latur | Gondia | Chhindwara | Chandrapur | Dharmapuri-TN | Faridkot | Dharwad | Daund | Chaksu | Bareilly | Kakinada | Haldwani | Doddaballapur | Dindori-MH | Bagru | Kudus | Kozhikode | Gurdaspur | Bokaro | Berhampur | Batala | Barrackpore | Ramgarh | Meerut | Bassi | Dera Bassi | Howrah | Karjat Raigarh | Thiruvananthapuram | Bheemunipatnam | Ambegoan | Allahabad | Aligarh | Alappuzha | Tirupathi | Thoppumpady | Srikakulam | Siliguri | Rourkela | Mirzapur | Gadag | Bellary | Tumkur | Sonipat | Hoshangabad | Junnar | Jalna | Hisar | Karnal | Kottayam | Muzzafarnagar | Ramnagara | Thrissur | Bahadurgarh | Balasore | Baraut | Dhar | Ernakulam | Gadhinglaj | Chikodi | Vaniyambadi | Kamothe |